





Get organised in three easy steps! If you save this site to your home screen, you will be able to find it quickly in class time.
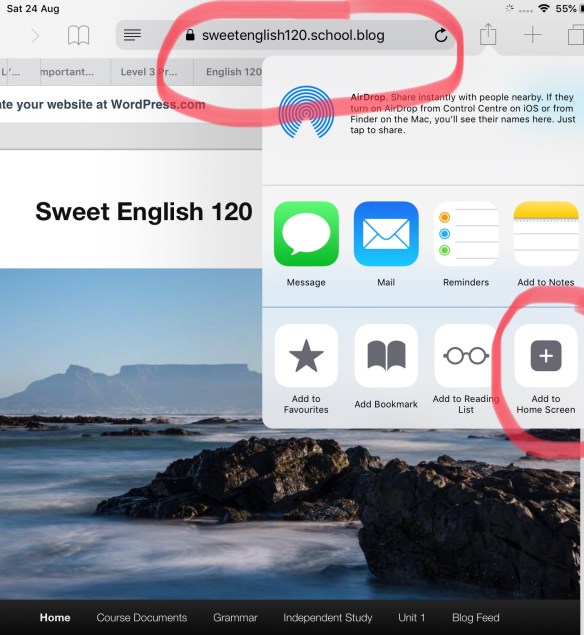
2. Follow our blog: Just click on the ‘Follow’ button at the bottom right hand side of the page and enter your university address when the dialogue box pops up. When you follow the blog you will get an email alert every time something new is posted.
3. Download the following Apps: Kahoot ( https://kahoot.it ) and Socrative ( https://b.socrative.com/login/student )


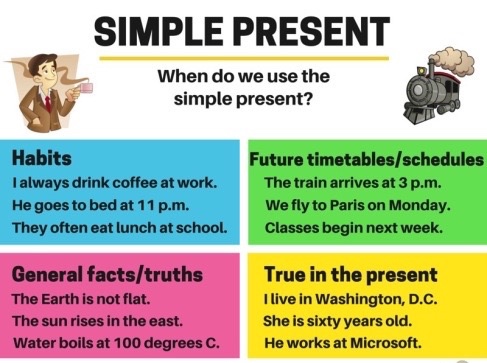
SIGNAL WORDS
We often find these words when the Present Simple Tense is used in a sentence:
NOTE: See sidebar for online exercise on this
REMEMBER: It is not as simple as just adding an ‘-s’. There are some spelling rules you have to remember.


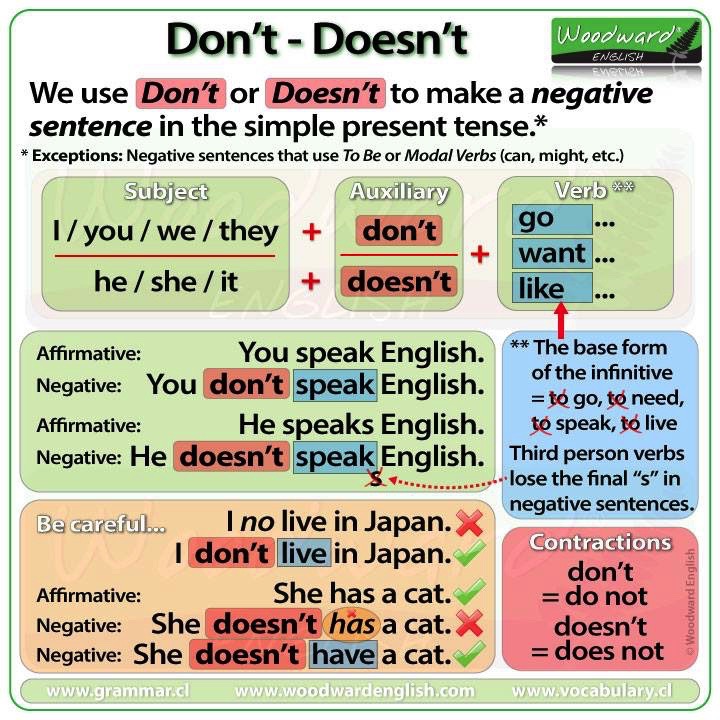
Now go to the sidebar and do these two exercises:

Information Questions in the Simple Present Tense
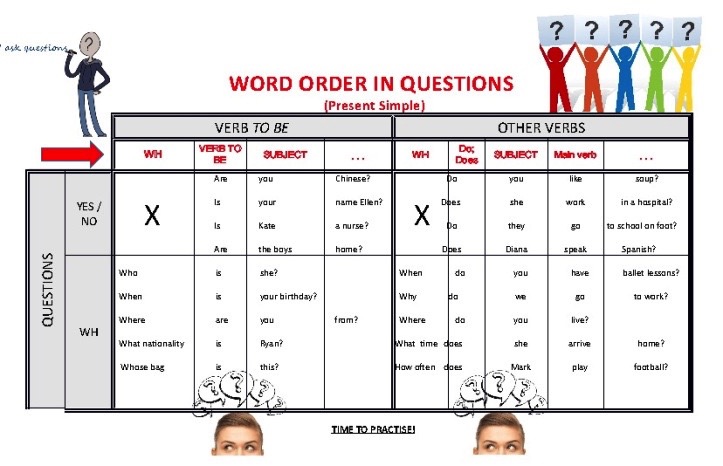
For more on Information Questions see under the Grammar Tab.
Watch this short video:
What is this bird doing? How? Why?
Read through the text below:
Use the dictionary to look up words you don’t know.
The kestrel is a small, chestnut brown bird of prey. It belongs to the falcon family. Kestrels are 32–39 cm (13–15 in) from head to tail. Their wings are 65–82 cm (26–32 in) when spread out. Females are larger. Kestrels are smaller than other birds of prey. Like the other members of the falcon family, they have long wings and a long tail. Their feathers are mainly light brown with black spots on the top and narrow blackish streaks on the underside. The kestrel’s hooked bill is a bluish colour with bit of yellow at the top. The legs are yellow.
The kestrel is unusual because it is the only bird of prey that can hover. When hunting, the kestrel hovers about 10–20 m (c.30–70 ft) above the ground. Kestrels have very good eyesight. They can see small prey from a distance. Once they see the prey, the bird makes a short, steep dive. They eat only mouse-sized mammals, large insects and small birds.
Kestrels are bold, and have adapted well to humans. They nest in buildings and hunt by main roads. Kestrels do not build their own nests, but use nests built by other birds.
‘Fun’ is a noun e.g. I had a lot of fun
‘Funny’ is an adjective e.g The joke was funny. She is a funny girl.
‘My holiday was relaxing. I felt really relaxed.’
Few, but common, adjectives end in either -ed or -ing:
worried / worrying, interested / interesting, excited / exciting
Adjectives that end in -ed are used to describe how people feel.
Examples:
‘He was surprised to find that he had been upgraded to first class.’
‘I was confused by the report.’
‘She felt tired after working hard all day.’
Adjectives that end in -ing are used to describe things and situations. Compare these example sentences to the ones above:
‘Being upgraded to first class is surprising.’
The findings of this report are confusing.’
‘Working hard all day is tiring.’
Online activities:
https://www.tolearnenglish.com/exercises/exercise-english-2/exercise-english-48887.php
Short quiz: Click on the link: Short quiz:







Part 1: Comparatives
Part 2: Superlatives

http://anthonyhalderman.com/english/compsup.htm
https://www.usingenglish.com/quizzes/45.html
http://www.softschools.com/quizzes/grammar/adjectives/quiz328.html
This site below has several additional links:
http://www.learnenglish-online.com/grammar/tests/superlativecomparative.html
http://www.tolearnenglish.com/exercises/exercise-english-2/exercise-english-12647.php
Short (10 questions) http://www.grammarbank.com/comparative-superlative-quiz.html

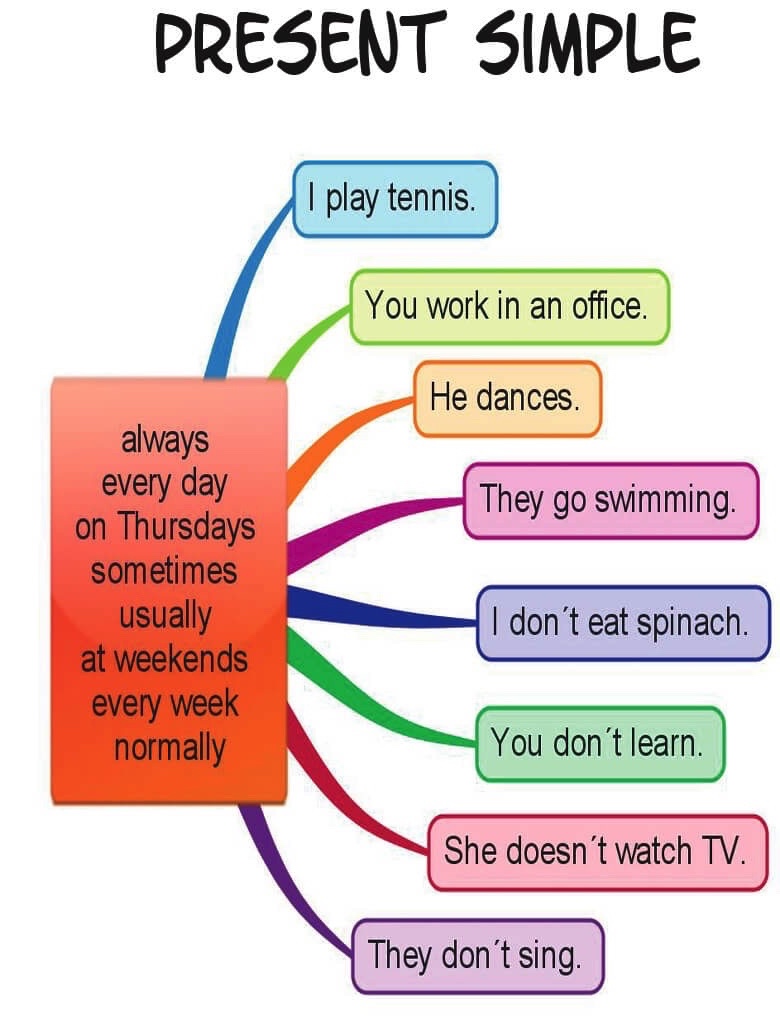
Look at the mind map below. It will help you to understand the difference between the Present Simple `and Present Continuous. Pay attention to the special SIGNAL WORDS used with these tenses.

You cannot form the Present Continuous unless you already know how to form the Present Simple of the verb ‘to be’. (is, am, are)
 See here for an explanation of the form and function of the Present Progressive Tense
See here for an explanation of the form and function of the Present Progressive Tense
The Present Continuous: Questions and Statements and Question Forms



There are some verbs that cannot be used in the Present Continuous Tense. We call these ‘stative verbs’. These “stative” verbs are about state, not action, and they cannot express the continuous aspect. Here are some of the most common non-continuous verbs:
feeling: hate, like, love, prefer, want, wish
senses: appear, feel, hear, see, seem, smell, sound, taste
communication: agree, deny, disagree, mean, promise, satisfy, surprise
thinking: believe, imagine, know, mean, realize, recognize, remember, understand
other states: be, belong, concern, depend, involve, matter, need, owe, own, possess
(See examples under the Grammar Tab)

https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/present-continuous-exercise-1.html
https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/present-continuous-exercise-2.html
https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/present-continuous-exercise-3.html
https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/present-continuous-exercise-4.html
https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/present-continuous-exercise-5.html
https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/present-continuous-exercise-6.html
https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/present-continuous-exercise-7.html
Present Simple or Present Continuous?
https://www.englisch-hilfen.de/en/exercises/tenses/simple_present_progressive2.htm
https://www.perfect-english-grammar.com/present-simple-present-continuous-1.html